Earwax removal - the benefits
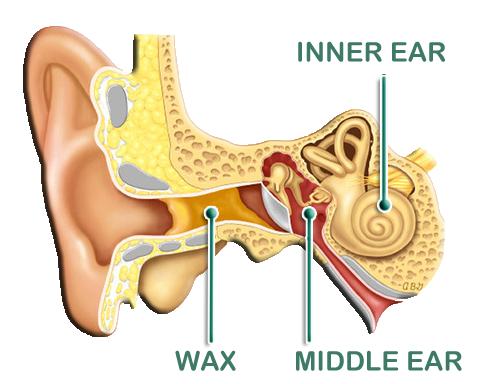
What exactly is earwax?
Earwax is a natural thick substance created by special cells in the ear. It's made of skin cells, fats, alcohol and cholesterol. It plays an important part in keeping the ear canal clean and healthy; it traps dust and small objects (including insects), helps to sterilize the ear, lubricates the skin and even clears itself out of the ear! Sometimes this self-clearing mechanism fails, perhaps due to too much hair, too much dust/dirt, use of cotton buds or bony growths in the ear (like swimmer's ear).
The effect of too much ear wax
Having too much wax can vary from a very mild inconvenience to a painful disability. The factors that determine its effect include; the amount of wax (the greater the wax the worse the effect), the shape of the wax (does it ‘seal’ the ear?), the position of the wax (is it touching the sensitive eardrum?), the density of the wax (is it compacted into a solid lump?), the age of the wax (older wax is harder and more likely to press against the ear canal when the jaw moves), is there something else with the wax (like a hearing aid ear tip, infectious material, dead skin, cotton wool, dirt/dust, a piece of Lego or a dead insect – yep, it happens!)?
The symptoms of excessive wax:
Looking inside your own ear is not an easy feat, and if you could, would you know exactly what you’re looking at? Instead, we rely on the symptoms of excessive wax:
- Reduced hearing, normally suddenly after water enters the ear
- Increased tinnitus (pronounced ‘Tin – it- us’, any noises generated inside your head)

- The sensation of feeling or hearing something moving in your ear
- A slight imbalance of sense of loss of equilibrium
- Your hearing doesn’t change when water gets in your ear
A buildup of earwax is like wearing earplugs and can dull your hearing. Alternatively some people experience intense itching deep inside the ear canal, but if you have pain, or are in doubt, then always check with an audiologist.
Ears blocked with wax can affect your hearing, trap water in your ears (increasing the risk of infection), and cause pain and imbalance. Blocked ears can also hide a multitude of conditions that need medical attention - so have your ears checked and cleared by an expert.
Signs and symptoms of earwax blockage may include:
- Earache
- Feeling of fullness in the affected ear
- Ringing or noises in the ear (tinnitus)
- Decreased hearing in the affected ear
- Dizziness